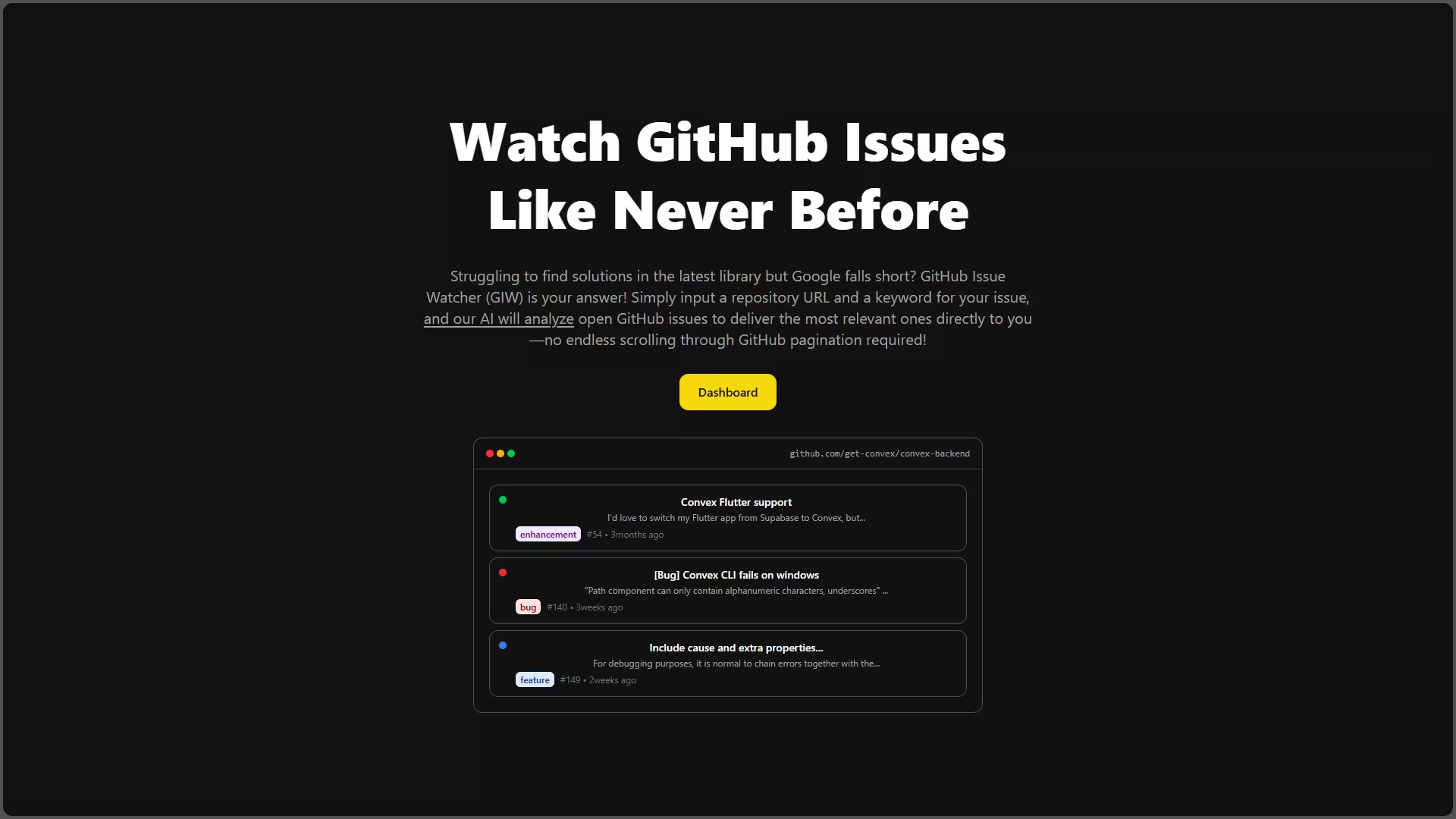
GitHub Issue Watcher is an intelligent issue monitoring platform that tracks GitHub repositories for keyword-matched issues and uses OpenAI to analyze relevance with precision scoring. It features a task queue system, rate limiting, batch processing, and automated email notifications—keeping developers informed without noise.
Why it matters
- AI relevance scoring: OpenAI analyzes each issue for true relevance (0-100 score), not just keyword matching—eliminates false positives
- Smart batching: Processes 1000 issues at a time with concurrent workers, optimized for provider rate limits
- Task queue system: Distributed worker architecture with locks, retries, and priority queueing
- Rate limiting: Per-user token and request tracking prevents API overuse
- Progressive emails: Send partial results every 200 issues, final digest on completion
- Real-time dashboard: Live updates via Convex with sortable tables and expand/collapse views
How it works (brief)
- User submits: GitHub repo URL + keyword (e.g., “bug”, “feature request”, “security”)
- Fetch issues: GitHub GraphQL API pulls all issues with pagination cursor
- Queue tasks: Each issue becomes a task in
analysis_taskstable - Worker processes: LLM worker picks tasks, calls OpenAI for relevance analysis
- Store results: Issues with scores saved to
reportstable - Email notifications: Resend sends progressive updates (every 200) + final digest
Stack
- Frontend: React 19 + TypeScript + Mantine UI
- Backend: Convex (serverless, real-time DB, cron jobs)
- Auth: Convex Auth (email/password + GitHub OAuth)
- GitHub API: Octokit GraphQL for issue fetching
- LLM: OpenAI (GPT-4o-mini for relevance analysis)
- Email: Resend with React Email templates
- Build: Rsbuild (Rspack)
The Problem: Noise in GitHub Issue Tracking
Developers monitoring GitHub repositories face critical challenges:
1. Keyword matching is too broad
Searching for “bug” returns:
- Actual bugs
- Feature requests mentioning “not a bug”
- Documentation updates about bug fixes
- Test cases for bug scenarios
- Unrelated discussions with “debug” in title
Result: 80% false positives, wasted time reviewing irrelevant issues.
2. Manual filtering doesn’t scale
- Large repos: 1000+ issues to review
- Multiple repos: Exponential complexity
- Label inconsistency: Not all maintainers use standardized labels
- Title ambiguity: “Fix #123” tells you nothing
Result: Developers miss critical issues or burn hours on manual triage.
3. Notification overload
- GitHub email notifications: All or nothing (can’t filter by relevance)
- Watch repos: Too noisy (every comment triggers notification)
- Custom queries: Limited to basic keyword/label filters
Result: Notification fatigue leads to ignoring important issues.
4. No context-aware understanding
Traditional keyword search can’t:
- Understand semantic meaning (“vulnerability” = “security issue”)
- Detect implied relevance (issue about “crash” is relevant to “stability”)
- Assess severity or urgency from tone/details
Result: Critical issues buried in noise.
The Solution: AI-Powered Issue Intelligence
GitHub Issue Watcher combines GitHub API automation with LLM analysis to deliver precision monitoring:
1. Smart Issue Fetching (GitHub GraphQL)
Why GraphQL over REST?
- Fetch only needed fields (reduce bandwidth)
- Paginate with cursor (efficient for large repos)
- Single query gets issues + labels (no N+1 problem)
Query structure:
query($owner: String!, $name: String!, $after: String) {
repository(owner: $owner, name: $name) {
issues(first: 100, after: $after, orderBy: {field: CREATED_AT, direction: DESC}) {
nodes {
id
number
title
body
labels(first: 10) {
nodes {
name
}
}
createdAt
}
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
}
}
}Implementation (simplified):
export const fetchAllIssues = action({
args: { repoUrl: v.string(), keyword: v.string() },
handler: async (ctx, args) => {
const [owner, name] = extractRepoDetails(args.repoUrl);
let cursor: string | null = null;
let allIssues: Issue[] = [];
do {
const result = await octokit.graphql(ISSUES_QUERY, { owner, name, after: cursor });
const issues = result.repository.issues.nodes;
// Filter by keyword (title + body contains keyword)
const matched = issues.filter(issue =>
issue.title.toLowerCase().includes(args.keyword.toLowerCase()) ||
issue.body?.toLowerCase().includes(args.keyword.toLowerCase())
);
allIssues.push(...matched);
cursor = result.repository.issues.pageInfo.hasNextPage
? result.repository.issues.pageInfo.endCursor
: null;
} while (cursor);
return allIssues;
}
});Batch processing: Fetches 100 issues per request, processes in batches of 1000 for memory efficiency.
2. AI Relevance Analysis (OpenAI)
Each issue is analyzed by GPT-4o-mini to determine true relevance:
Prompt engineering:
const systemPrompt = `
You are a GitHub issue relevance analyzer. Given a keyword and an issue, determine:
1. Relevance score (0-100):
- 0-20: Completely irrelevant (keyword coincidentally appears)
- 21-40: Tangentially related (mentions topic but not main focus)
- 41-60: Somewhat relevant (related to topic but not actionable)
- 61-80: Relevant (directly addresses topic)
- 81-100: Highly relevant (critical issue matching keyword intent)
2. Explanation: 1-2 sentence justification (max 260 chars)
3. Matched terms: Specific phrases/words that triggered relevance
4. Evidence: Direct quotes from issue supporting the score
Return JSON:
{
"relevanceScore": 85,
"explanation": "Issue reports critical security vulnerability in authentication...",
"matchedTerms": ["security", "authentication bypass", "CVE"],
"evidence": ["User can bypass login with malformed request", "Affects all versions"]
}
`;
const userPrompt = `
Keyword: "${keyword}"
Issue #${issue.number}: ${issue.title}
Labels: ${issue.labels.join(", ")}
Body:
${issue.body.slice(0, 3000)} // Truncate to avoid token limits
Analyze relevance.
`;Non-multiple-of-5 enforcement: Scores are adjusted ±1 if divisible by 5 (prevents LLM bias toward round numbers like 50, 75, 80).
Retry logic with exponential backoff:
async function safeAnalyzeIssue(openai, prompt, model, issue) {
for (let attempt = 1; attempt <= MAX_RETRIES; attempt++) {
try {
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model,
messages: [
{ role: "system", content: systemPrompt },
{ role: "user", content: prompt }
],
temperature: 0.3, // Lower temp for consistency
max_tokens: 300
});
const text = response.choices[0].message.content;
return extractAndParseJSON(text);
} catch (error) {
if (attempt === MAX_RETRIES) throw error;
const delay = Math.pow(2, attempt) * 1000; // 2s, 4s, 8s
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
}
}
}Response parsing: Handles multiple formats (clean JSON, fenced code blocks, inline JSON strings).
3. Task Queue System with Distributed Workers
Architecture:
User submits query → Fetch GitHub issues → Enqueue analysis tasks →
Workers process concurrently → Store results → Send emailTask lifecycle:
- Created: Issue added to
analysis_taskstable with status “queued” - Queued: Awaiting worker pickup
- Running: Worker acquired task (locked)
- Completed: Analysis finished, result stored
- Failed: Max retries exhausted
Worker implementation:
export const processWorkBatch = internalAction({
args: { batchSize: v.number() },
handler: async (ctx, args) => {
// Acquire distributed lock (prevent concurrent workers on same report)
const locked = await ctx.runMutation(api.llmWorker.acquireLock, {
name: "llmWorker",
ttlMs: 60000 // 60s lease
});
if (!locked) return { processed: 0 };
try {
// Select tasks from queue (priority + FIFO)
const tasks = await ctx.runQuery(api.queue.selectQueuedTasks, {
limit: args.batchSize
});
// Mark as running
await ctx.runMutation(api.llmWorker.markTasksRunning, {
taskIds: tasks.map(t => t._id)
});
// Process concurrently (max 3 to avoid rate limits)
const chunks = chunkArray(tasks, MAX_CONCURRENT);
for (const chunk of chunks) {
await Promise.all(
chunk.map(task => processTask(ctx, task))
);
}
return { processed: tasks.length };
} finally {
// Release lock
await ctx.runMutation(api.llmWorker.releaseLock, {
name: "llmWorker"
});
}
}
});Cron job: Runs every 5 minutes to process pending tasks.
crons.interval(
"process llm tasks",
{ minutes: 5 },
internal.llmWorker.processWorkBatch,
{ batchSize: 10 }
);4. Rate Limiting (Token + Request Tracking)
Why rate limit?
- OpenAI: 10k RPM, 2M TPM (tokens per minute) on paid tier
- GitHub: 5k requests/hour for authenticated users
- Prevent single user from exhausting quota
Implementation:
export const checkRateLimit = mutation({
args: {
userId: v.id("users"),
requestCost: v.number(), // Number of requests
tokenCost: v.number() // Estimated tokens
},
handler: async (ctx, args) => {
const bucket = `user:${args.userId}`;
const now = Date.now();
const WINDOW_MS = 60000; // 1 minute
let limit = await ctx.db
.query("rate_limits")
.withIndex("bucket", q => q.eq("bucket", bucket))
.first();
if (!limit) {
// Create new bucket
limit = await ctx.db.insert("rate_limits", {
bucket,
requests: 0,
tokens: 0,
updatedAt: now
});
}
// Reset if window expired
if (now - limit.updatedAt > WINDOW_MS) {
await ctx.db.patch(limit._id, {
requests: 0,
tokens: 0,
updatedAt: now
});
limit = { ...limit, requests: 0, tokens: 0 };
}
// Check limits
const MAX_REQUESTS_PER_MIN = 100;
const MAX_TOKENS_PER_MIN = 50000;
if (limit.requests + args.requestCost > MAX_REQUESTS_PER_MIN) {
throw new ConvexError("Rate limit exceeded: too many requests");
}
if (limit.tokens + args.tokenCost > MAX_TOKENS_PER_MIN) {
throw new ConvexError("Rate limit exceeded: too many tokens");
}
// Update bucket
await ctx.db.patch(limit._id, {
requests: limit.requests + args.requestCost,
tokens: limit.tokens + args.tokenCost,
updatedAt: now
});
return { allowed: true };
}
});Token estimation: title.length + body.length + 500 (rough heuristic).
5. Progressive Email Notifications (Resend)
Strategy: Send partial results every 200 issues to keep user informed during long-running jobs.
Email types:
- Partial digest: After every 200 analyzed issues
- Final digest: When all issues processed
- Error notification: If job fails
Template (React Email):
export function IssueReportEmail({
repoUrl,
keyword,
issues,
isPartial
}: {
repoUrl: string;
keyword: string;
issues: Issue[];
isPartial: boolean;
}) {
const highRelevance = issues.filter(i => i.relevanceScore >= 70);
const mediumRelevance = issues.filter(i => i.relevanceScore >= 40 && i.relevanceScore < 70);
return (
<Html>
<Head />
<Body>
<Container>
<Heading>
{isPartial ? "Partial Report" : "Final Report"}: {keyword}
</Heading>
<Text>Repository: {repoUrl}</Text>
<Text>Total issues analyzed: {issues.length}</Text>
<Section>
<Heading as="h2">High Relevance ({highRelevance.length})</Heading>
{highRelevance.map(issue => (
<Row key={issue.id}>
<Column>
<Link href={`${repoUrl}/issues/${issue.number}`}>
#{issue.number}: {issue.title}
</Link>
<Text>Score: {issue.relevanceScore}/100</Text>
<Text>{issue.explanation}</Text>
<Hr />
</Column>
</Row>
))}
</Section>
<Section>
<Heading as="h2">Medium Relevance ({mediumRelevance.length})</Heading>
{/* Similar structure */}
</Section>
{isPartial && (
<Text>
<strong>This is a partial report.</strong> Analysis continues in background.
You'll receive the final report when complete.
</Text>
)}
</Container>
</Body>
</Html>
);
}Sending logic:
export const sendProgressiveEmail = mutation({
args: {
reportId: v.id("reports"),
currentIssueCount: v.number()
},
handler: async (ctx, args) => {
const report = await ctx.db.get(args.reportId);
const BATCH_SIZE = 200;
// Send partial email every 200 issues
if (args.currentIssueCount % BATCH_SIZE === 0) {
await ctx.scheduler.runAfter(0, internal.resend.sendIssueReport, {
reportId: args.reportId,
isPartial: true
});
// Update last email sent timestamp
await ctx.db.patch(args.reportId, {
lastPartialEmailAt: Date.now(),
emailsSent: (report.emailsSent || 0) + 1
});
}
}
});Database Schema
Core Tables
reports: Stores completed analysis results
reports: defineTable({
repoUrl: v.string(), // e.g., "https://github.com/facebook/react"
keyword: v.string(), // Search term
userEmail: v.string(),
userId: v.id("users"),
issues: v.array(v.object({
id: v.string(), // GitHub issue ID
number: v.number(), // Issue number
title: v.string(),
body: v.string(),
labels: v.array(v.string()),
createdAt: v.string(),
relevanceScore: v.number(), // 0-100 (AI-scored)
explanation: v.string(), // AI reasoning
matchedTerms: v.optional(v.array(v.string())),
evidence: v.optional(v.array(v.string()))
})),
createdAt: v.number(),
lastFetched: v.number(),
batchCursor: v.optional(v.string()), // GitHub pagination cursor
isComplete: v.boolean(),
isCanceled: v.optional(v.boolean()),
emailsSent: v.optional(v.number()),
lastPartialEmailAt: v.optional(v.number())
})
.index("userEmail", ["userEmail"])
.index("userId", ["userId"])
.index("repoUrl_keyword", ["repoUrl", "keyword"])analysis_tasks: Task queue for LLM workers
analysis_tasks: defineTable({
reportId: v.id("reports"),
ownerUserId: v.id("users"),
keyword: v.string(),
issue: v.object({
id: v.string(),
number: v.number(),
title: v.string(),
body: v.string(),
labels: v.array(v.string()),
createdAt: v.string()
}),
estTokens: v.number(), // Estimated token cost
status: v.string(), // queued, running, completed, failed
priority: v.number(), // Lower = higher priority
attempts: v.number(), // Retry counter
error: v.optional(v.string()),
createdAt: v.number(),
updatedAt: v.number()
})
.index("status_priority", ["status", "priority"])
.index("report_status", ["reportId", "status"])
.index("owner_status", ["ownerUserId", "status"])rate_limits: Per-user rate tracking
rate_limits: defineTable({
bucket: v.string(), // "user:userId"
requests: v.number(),
tokens: v.number(),
updatedAt: v.number()
})
.index("bucket", ["bucket"])locks: Distributed locks for workers
locks: defineTable({
name: v.string(), // Lock identifier
leaseExpiresAt: v.number(), // Expiry timestamp
owner: v.optional(v.string()) // Worker ID
})
.index("name", ["name"])Frontend Architecture
Pages & Components
Dashboard (/):
- Authentication form (email/password + GitHub OAuth)
- Issue form modal (submit repo URL + keyword)
- Reports list (all user reports)
- Issues table (expandable rows with details)
Key components:
- IssueFormModal:
function IssueFormModal({ onReportGenerated }) {
const [repoUrl, setRepoUrl] = useState("");
const [keyword, setKeyword] = useState("");
const submitQuery = useMutation(api.githubIssues.submitQuery);
const handleSubmit = async () => {
const reportId = await submitQuery({ repoUrl, keyword });
onReportGenerated(reportId);
};
return (
<Modal opened={opened} onClose={close}>
<TextInput label="Repository URL" value={repoUrl} onChange={setRepoUrl} />
<TextInput label="Keyword" value={keyword} onChange={setKeyword} />
<Button onClick={handleSubmit}>Start Monitoring</Button>
</Modal>
);
}- ReportsList:
function ReportsList({ reportId, setReportId }) {
const reports = useQuery(api.githubIssues.listReports);
return (
<Stack>
{reports?.map(report => (
<Card
key={report._id}
onClick={() => setReportId(report._id)}
className={reportId === report._id ? "selected" : ""}
>
<Text fw={700}>{report.keyword}</Text>
<Text size="sm">{report.repoUrl}</Text>
<Badge color={report.isComplete ? "green" : "yellow"}>
{report.isComplete ? "Complete" : "Processing"}
</Badge>
<Text size="xs">{report.issues.length} issues</Text>
</Card>
))}
</Stack>
);
}- IssuesTable:
function IssuesTable({ reportId }) {
const report = useQuery(api.githubIssues.getReport, { reportId });
const [sortedIssues, setSortedIssues] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
// Sort by relevance score (descending)
const sorted = [...(report?.issues || [])].sort(
(a, b) => b.relevanceScore - a.relevanceScore
);
setSortedIssues(sorted);
}, [report]);
return (
<Table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Issue</th>
<th>Relevance</th>
<th>Explanation</th>
<th>Labels</th>
<th>Created</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{sortedIssues.map(issue => (
<tr key={issue.id}>
<td>
<Anchor href={`${report.repoUrl}/issues/${issue.number}`} target="_blank">
#{issue.number}: {issue.title}
</Anchor>
</td>
<td>
<Badge color={getScoreColor(issue.relevanceScore)}>
{issue.relevanceScore}
</Badge>
</td>
<td>{issue.explanation}</td>
<td>
{issue.labels.map(label => (
<Badge key={label} size="sm">{label}</Badge>
))}
</td>
<td>{formatDate(issue.createdAt)}</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</Table>
);
}Real-time updates: Convex queries auto-refresh when data changes (no polling needed).
Key Design Decisions
Why OpenAI for Relevance Scoring?
Alternatives:
- Keyword matching: Too broad, 80% false positives
- Label filtering: Inconsistent across repos, requires manual setup
- Embeddings + similarity: Requires vector DB, slower, less explainable
- Rule-based ML: Needs training data, brittle
OpenAI wins:
- Semantic understanding (detects relevance even without exact keyword)
- Explainable scores (provides reasoning in natural language)
- No training data needed (zero-shot learning)
- Fast inference (< 1s per issue)
- Cost-effective (GPT-4o-mini: $0.15/1M input tokens)
Why Task Queue vs. Direct Processing?
Direct processing issues:
- Long-running requests timeout (Convex Actions: 5min limit)
- No retry on failure
- Blocking (user waits for all issues)
Task queue benefits:
- Resilient (tasks persist across failures)
- Scalable (multiple workers process concurrently)
- Interruptible (user can cancel, progress saved)
- Progressive feedback (partial results sent via email)
Why Convex Backend?
Alternatives:
- Firebase: No serverless functions for complex logic
- Supabase: PostgreSQL not ideal for real-time + task queues
- Custom Express + MongoDB: More setup, no built-in auth/cron
Convex advantages:
- Real-time queries (no polling, WebSocket under the hood)
- Serverless functions (actions, queries, mutations)
- Integrated auth (email/password + OAuth)
- Cron jobs (scheduled workers)
- TypeScript-first (auto-generated types)
- Horizontal scaling (no server management)
Why Progressive Emails?
User feedback: “I submitted a query for 2000 issues and heard nothing for 20 minutes. I thought it crashed.”
Solution: Send partial digests every 200 issues (10-20 seconds of processing).
Benefits:
- Transparency (user sees progress)
- Early insights (high-relevance issues surfaced immediately)
- Reduced anxiety (no “black box” wait)
Trade-off: More emails, but each provides value.
Performance Optimizations
Backend
- Batch processing: Analyze 1000 issues at a time (avoid memory overflow)
- Concurrent workers: Max 3 simultaneous OpenAI calls (respect rate limits)
- Indexed queries: All filter fields have indexes (status, priority, userId)
- Cursor pagination: GitHub API uses cursors (efficient for large repos)
- Token estimation: Pre-calculate to enforce rate limits before API call
- Lock-based coordination: Prevents duplicate work across multiple cron runs
Frontend
- Code splitting: Lazy load dashboard (separate auth chunk)
- Memoization: Sorted issues cached with useMemo
- Virtualization: Large tables use react-window (render only visible rows)
- Optimistic updates: UI updates immediately on mutation (rollback on error)
LLM Optimization
- Temperature: 0.3 (lower = more consistent scores)
- Max tokens: 300 (limits response length, reduces cost)
- Body truncation: Send only first 3000 chars (most relevant info in top)
- Retry strategy: Exponential backoff (2s, 4s, 8s) on 429 rate limit
Future Enhancements
Advanced Features
- Multi-repo monitoring: Track multiple repos in single query
- Label filtering: Pre-filter issues by labels before LLM analysis
- Slack integration: Send notifications to Slack channels
- Trend detection: Analyze issue patterns over time (e.g., spike in “crash” issues)
- Webhook triggers: Real-time monitoring (GitHub webhook → instant analysis)
UX Improvements
- Score calibration: User feedback to tune relevance thresholds
- Saved queries: Bookmark frequently monitored repos
- Export: Download results as CSV/JSON
- Dark mode: System preference detection
Infrastructure
- Horizontal scaling: Multiple worker instances for high throughput
- Priority tiers: Premium users get faster processing
- Cost analytics: Show token usage per report
Architecture Diagram
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ FRONTEND (React) │
│ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ │
│ │ Issue Form │ │ Reports List │ │ Issues Table │ │
│ │ (Submit) │ │ (Real-time) │ │ (Sortable) │ │
│ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └──────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
│ Convex Real-time Queries
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ CONVEX BACKEND │
│ ┌───────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ │
│ │ Queries │ │ Mutations │ │ Actions │ │
│ │ (read DB) │ │ (write DB) │ │ (external) │ │
│ └───────────────┘ └──────────────┘ └─────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ DATABASE │ │
│ │ • reports (user queries + results) │ │
│ │ • analysis_tasks (queue) │ │
│ │ • rate_limits (per-user tracking) │ │
│ │ • locks (worker coordination) │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ CRON JOBS (Every 5 minutes) │ │
│ │ • Process task queue (LLM worker) │ │
│ │ • Vacuum expired tasks (cleanup) │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│ │ │
│ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼
┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ GitHub API │ │ OpenAI GPT-4o │ │ Resend │
│ (GraphQL) │ │ (Relevance) │ │ (Email) │
└──────────────┘ └──────────────────┘ └──────────────┘Security & Best Practices
API Keys
- GitHub token: Required for authenticated API calls (5k req/hour vs 60/hour unauthenticated)
- OpenAI key: Server-side only (never exposed to client)
- Resend key: Server-side only
Rate Limiting
- Per-user limits: Prevent single user from exhausting quota
- Token estimation: Pre-check before LLM call
- Graceful degradation: Return cached results if rate limit hit
Authentication
- Convex Auth: Built-in email verification + OAuth
- Session management: Secure tokens with auto-refresh
- Password hashing: Bcrypt with salt
Data Privacy
- No issue content storage: Only metadata (title, number) stored permanently
- Rate limit data: Auto-expires after 1 hour
- User data deletion: GDPR-compliant account deletion